Mechanical engineering is one of the most versatile and...
When it comes to window replacement in New Jersey,...
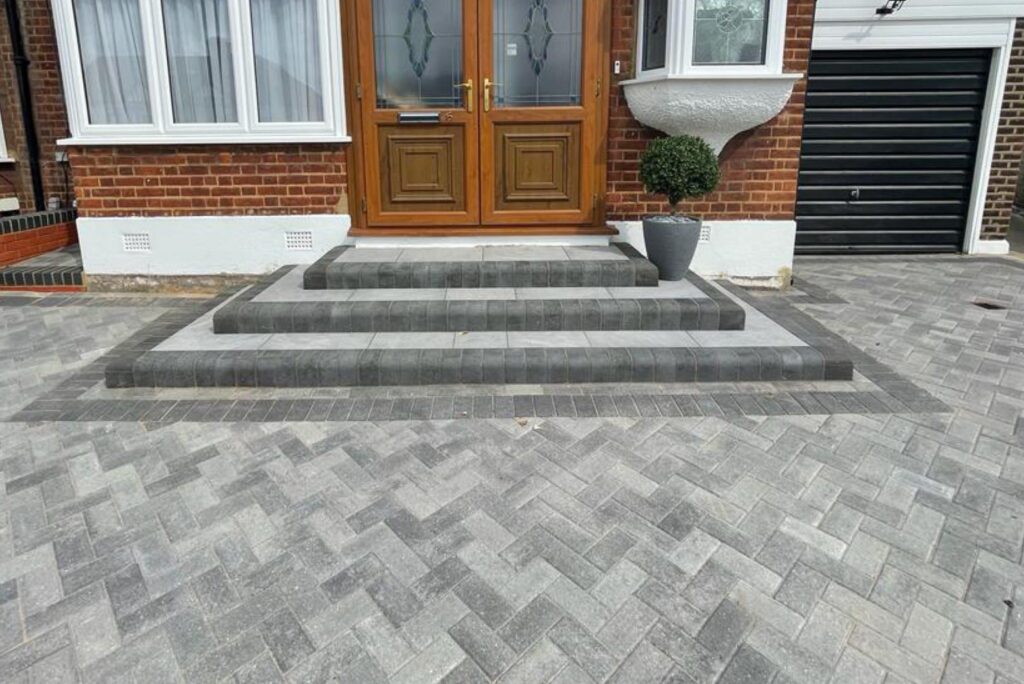
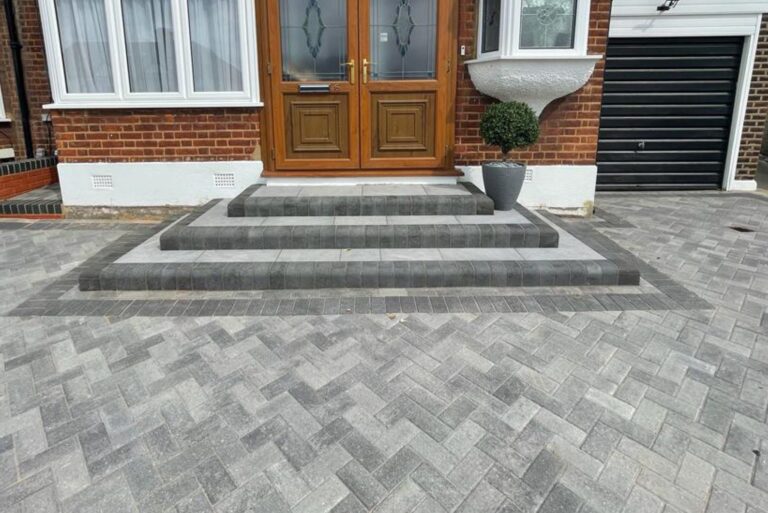
Thinking of installing a new driveway, patio, or path...
For business owners, sending sales invoices to their clients...
Gold has long been considered one of the most...
Maintaining a brand image is crucial for all businesses....
In Australia, students have to forego all the challenges...
In today’s highly competitive hospitality industry, a solid SEO...
The Char Dham Yatra is a spiritual journey that...
Introduction: Celebrate your baby’s special day with the best...