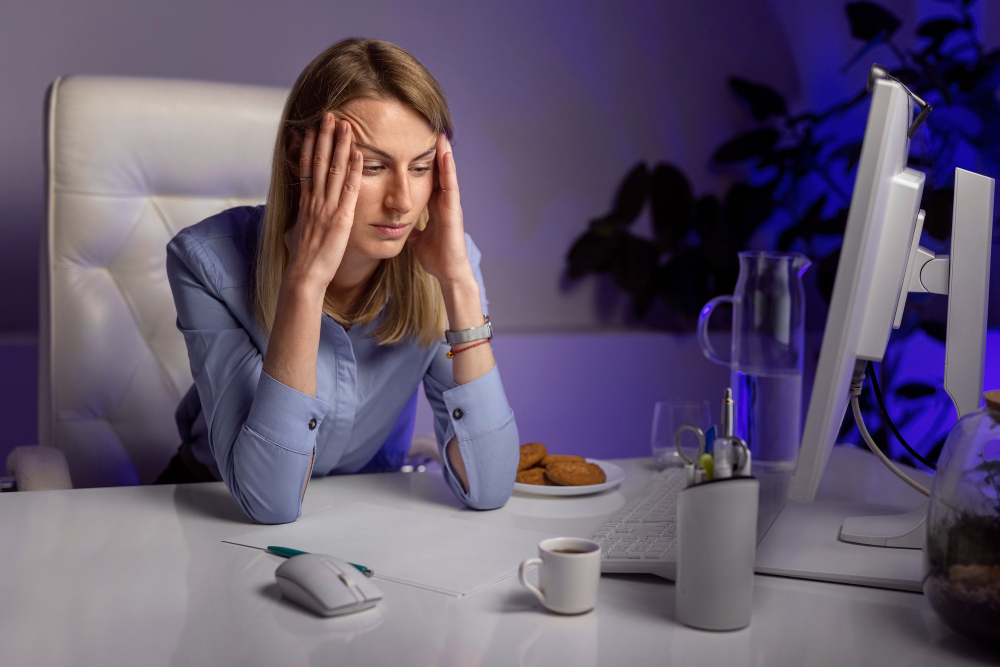
Screens have become an unavoidable part of modern life. From smartphones and laptops to tablets and televisions, most people spend a large portion of their day connected to digital devices. While technology improves convenience and productivity, excessive exposure can lead to digital overload — a state where constant screen interaction begins to affect brain health, focus, and emotional well-being.
Understanding how screen time impacts the brain and why reducing screen time is important can help create a healthier balance between the digital and real worlds.
What Happens to Your Brain During Screen Exposure
Digital devices are designed to capture attention. Notifications, social media updates, videos, and games stimulate the brain’s reward system by releasing dopamine, a chemical linked to pleasure and motivation. While this feels satisfying, constant stimulation can make the brain dependent on fast, high-reward digital input.
Over time, this reduces the brain’s tolerance for slower activities like reading, deep thinking, or face-to-face conversations. The brain becomes conditioned to seek quick rewards, making concentration more difficult. Continuous screen engagement also increases cognitive load, forcing the brain to process large amounts of information rapidly, which can lead to mental fatigue.
Negative Effects of Excessive Screen Time
Reduced Attention Span
Frequent multitasking between apps, messages, and tabs trains the brain to shift focus constantly. This weakens the ability to concentrate on one task for extended periods.
Memory and Learning Challenges
Relying heavily on digital devices for information storage can reduce memory retention. When people know information is easily searchable, the brain invests less effort in remembering it.
Sleep Disruption
Exposure to blue light from screens suppresses melatonin production — the hormone responsible for sleep. This makes it harder to fall asleep and affects sleep quality, leading to daytime fatigue.
Increased Stress and Anxiety
Constant connectivity creates pressure to respond quickly and stay updated. Social media comparisons and information overload can also increase anxiety and emotional stress.
Eye Strain and Headaches
Long screen sessions may cause dry eyes, blurred vision, and headaches, contributing to physical discomfort and reduced productivity.
How Screen Time Affects Different Age Groups
Children
Developing brains are especially vulnerable. Too much screen exposure may affect attention span, language development, and social skills. Children may also become less physically active.
Adults
Working adults often spend hours in front of screens, leading to mental exhaustion, reduced productivity, and burnout. The inability to disconnect can increase stress levels.
Older Adults
For older individuals, excessive screen time may disrupt sleep patterns and reduce real-life social interaction, impacting emotional health.
Signs You May Be Experiencing Digital Overload
If you notice the following symptoms, your brain may need a break:
- Constant tiredness or mental fog
- Difficulty concentrating
- Mood swings or irritability
- Trouble sleeping
- Feeling overwhelmed by information
These signs suggest it may be time to prioritize reducing screen time to allow the brain to recover.
Benefits of Reducing Screen Time
Making a conscious effort toward reducing screen time offers several mental and physical benefits:
- Improved focus and productivity
- Better sleep quality and deeper rest
- Lower stress and anxiety levels
- Enhanced creativity and mental clarity
- Stronger personal relationships
When the brain is not constantly stimulated, it can reset, process information more effectively, and function more efficiently.
Practical Tips for Reducing Screen Time
Set Daily Screen Limits
Use built-in digital wellbeing tools or apps to track and limit non-essential usage.
Establish Digital-Free Zones
Keep devices away from the dining table and bedroom to promote mindful living and better sleep.
Avoid Screens Before Bed
Stop using devices at least one hour before sleep to allow melatonin levels to rise naturally.
Replace Screen Habits
Engage in offline activities such as reading, walking, exercising, or spending time with family and friends.
Practice Mindful Usage
Before picking up a device, ask yourself if it’s necessary or simply a habit triggered by boredom.
Take Regular Breaks
Follow the 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, look 20 feet away for 20 seconds to reduce eye strain.
Conclusion
Technology is a powerful tool, but excessive use can negatively impact brain function, attention, sleep, and emotional balance. Digital overload is becoming increasingly common, making reducing screen time an essential step toward better mental and physical health.
Small daily changes — such as setting boundaries, creating screen-free time, and engaging in offline activities — can significantly improve brain performance and overall well-being. For more expert-backed wellness insights and practical health guidance, platforms like 365LivingHealthy continue to inspire individuals to make smarter lifestyle choices and maintain a healthier balance in a technology-driven world.